Difference between revisions of "X engine"
m |
m |
||
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | + | {{X}} | |
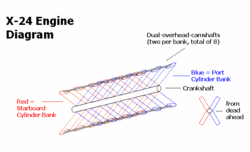
[[Image:X-24-engine.GIF|thumb|right|250px|<center>A simplified diagram of an X24 engine</center>]] | [[Image:X-24-engine.GIF|thumb|right|250px|<center>A simplified diagram of an X24 engine</center>]] | ||
| + | |||
An '''X engine''' is a [[piston engine]] comprising twinned [[v_engine|V-block engines]] horizontally-opposed to each other. Thus, the cylinders are arranged in four banks, driving a common [[crankshaft]]. Viewed head-on, this would appear as an X. Since [[24-cylinder]] models were the predominant configuration, it is most likely (but not known) that the angles between banks would have been 60-120-60-120, and not 90-90-90-90, since V-12 engines most commonly use a 60-degree bank to improve [[engine vibration]] characteristics. X-engines were often [[coupled engines]] derived from existing powerplants. | An '''X engine''' is a [[piston engine]] comprising twinned [[v_engine|V-block engines]] horizontally-opposed to each other. Thus, the cylinders are arranged in four banks, driving a common [[crankshaft]]. Viewed head-on, this would appear as an X. Since [[24-cylinder]] models were the predominant configuration, it is most likely (but not known) that the angles between banks would have been 60-120-60-120, and not 90-90-90-90, since V-12 engines most commonly use a 60-degree bank to improve [[engine vibration]] characteristics. X-engines were often [[coupled engines]] derived from existing powerplants. | ||
| Line 24: | Line 25: | ||
| − | + | {{Automobile configurations}} | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
{{Piston engine configurations}} | {{Piston engine configurations}} | ||
| + | {{Machine configurations|state=uncollapsed}} | ||
Latest revision as of 09:26, 8 October 2009
An X engine is a piston engine comprising twinned V-block engines horizontally-opposed to each other. Thus, the cylinders are arranged in four banks, driving a common crankshaft. Viewed head-on, this would appear as an X. Since 24-cylinder models were the predominant configuration, it is most likely (but not known) that the angles between banks would have been 60-120-60-120, and not 90-90-90-90, since V-12 engines most commonly use a 60-degree bank to improve engine vibration characteristics. X-engines were often coupled engines derived from existing powerplants.
This configuration is extremely uncommon, primarily due its weight and complexity as compared to a radial engine. However, it was more compact (per number of cylinders) than a V-engine. In practice, the X-engine inherited the drawbacks of both inline and radial designs rather than their advantages. Overheating was a perpetual problem for X engines, and a major reason for the failure of the type.
Most examples of X-engines are from the World War II era, and were designed for large military aircraft. The following are examples of this engine type:
- Isotta-Fraschini Zeta R.C. 24/60, an X-24 developed for the Caproni F6 fighter, but never fully completed before Italy’s surrender in 1943.
- Daimler Benz DB 604, an X-24 developed for the Luftwaffe’s Bomber B program. Development suspended.
- Rolls-Royce Vulture, an X-24 based on two Peregrines and the powerplant of the ill-fated Avro Manchester bomber and the Hawker Tornado fighter.
- Napier Cub, a water cooled X-16 engine of the 1920's, which powered the prototype Blackburn Cubaroo torpedo bomber.
| Piston engine configurations | |
|---|---|
| Straight | Single, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 8, 9, 10, 12, 14 |
| V | 2, 4, 5, 6, 8, 10, 12, 16, 20, 24 |
| Flat | 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 16, H |
| W | 8, 9, 12, 16, 18 |
| Other inline | H, VR, Opposed, U (Square), X |
| Other | Hemi, Radial, Rotary, Pistonless, Deltic, (Wankel) |
| Heat engines | |
|---|---|
| Stroke cycles One • Two • Four • Six • | |
| Engine types Gas turbine • Piston • Jet • Rocket engine • Steam engine • Stirling engine • Tschudi• Twingle Rotary • Wankel • Free-piston • Britalus • Coomber • Swing-piston • Orbital • Quasiturbine | |
| Valves Cylinder head porting • D slide • Four-stroke • Manifold • Multi • Piston • Poppet • Sleeve | |
| Piston layouts Single cylinder • Straight • Opposed • Flat • V • W • H • Deltic • Radial • Rocket engine nozzle • Rotary • Stelzer • Controlled Combustion • Bourke | |
| Motion mechanisms Cam • Connecting rod • Coomber rotary • Crank • Crank substitute • Crankshaft • Linkages (Evans • Peaucellier-Lipkin • Sector straight-line • Watt) • Double acting/differential cylinder | |
| Thermodynamic cycle |